티스토리 뷰
AOP
Aspect Oriented Programming의 약자입니다. aspect는 부가기능을 의미합니다. 즉 여러객체에 공통으로 적용할 수 있는 기능을 분리해서 재사용성을 높여주는 프로그래밍 기법입니다. 스프링은 이를 proxy객체를 사용함으로써 aop를 실현합니다.
AOP 주요 용어들
Target
부가기능을 부여할 대상 객체를 의미합니다. 스프링에서는 주로 Service 객체들이 이에 해당합니다.
Advice
실질적인 부가기능을 담은 구현체를 의미합니다. Aspect가 언제 무엇을 할지를 결정합니다. '언제'에 따라 advice는 5가지 종류로 나눌 수 있습니다.
JoinPoint
프로그램의 실행중 Advice가 삽입될 수 있는 모든 위치들을 의미합니다. 메서드 호출, 예외 호출 등이 이에 해당하며 스프링에서는 프록시를 사용하여 AOP를 실현하므로 다른 프레임워크와는 달리 메서드만이 Joinpoint가 될 수 있습니다.
Pointcut
Advice를 적용할 대상(메서드)를 선정하는 방법을 말합니다. 즉 Advice를 적용할 Joinpoint를 선정하는 모듈을 의미합니다.
Aspect
부가기능 모듈을 Aspect라고 부르며, 핵심기능에 부가되어 의미를 갖는 특별한 모듈이라 생각하시면 됩니다. Aspect는 부가될 기능을 정의한 Advice와 Advice를 어디에 적용할지를 결정하는 Pointcut을 함께 갖고 있습니다.
스프링 AOP 구현
Aspect로 사용할 클래스에 @Aspect 어노테이션을 붙이고 @Poincut을 통해 타겟 메서드에서 advice와 결합할 메서드를 결정하고 언제 어떤 메서드를 적용할지 @Around 로 결정하면 됩니다. 아래 예제에선 가장 많이 사용되는 Around advice를 사용한 예시입니다.
package apsect;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class ExeTimeAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * chap07..*(..))")
private void publicTarget() {}
@Around("publicTarget()")
public Object measure(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
return result;
} finally {
long finish=System.nanoTime();
System.out.printf("실행시간: %d\n",finish-start);
}
}
}
@Pointcut의 값으로 설정한 execution 명시자는 chap07를 포함한 그 하위 패키지에 속한 빈 객체의 public 메서드를 pointcut으로 설정합니다.
@Around 는 Around Advice를 정의합니다. 어노테이션 값으로 publicTarget()을 사용하는데, 이는 pointcut으로 설정된 public 메서드에 아래서 정의하는 메서드를 적용하는 의미입니다.
설정 클래스를 적용하면 다음과 같습니다.
package config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
import apsect.ExeTimeAspect;
import chap07.Calculator;
import chap07.REcCalculator;
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppCtx {
@Bean
public ExeTimeAspect exeTimeAspect() {
return new ExeTimeAspect();
}
@Bean
public Calculator calculator() {
return new REcCalculator();
}
}
@EnalbeAspectJAutoProxy 어노테이션은 스프링이 @Apsect 어노테이션이 붙은 빈 객체를 찾아 해당 객체의 @Poincut과 @Around 설정을 사용하게 됩니다.
package main;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import chap07.Calculator;
import config.AppCtx;
public class MainAspect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppCtx.class);
Calculator cal = ctx.getBean("calculator",Calculator.class);
cal.factorial(5);
System.out.println(cal.getClass().getName());
}
}
실행하게 되면 아래와 같은 화면이 출력됩니다.
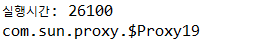
유의할 것은 객체의 클래스 이름인 REcCalculator이 출력되는 것이 아니라 Proxy 타입이 출력되는 것입니다. 이 타입은 스프링이 실행시간 도중 생성한 proxy타입입니다.
참고자료
'Books > 스프링5 프로그래밍 입문' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 스프링 MVC 시작하기 (0) | 2021.03.20 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] AOP (2) (0) | 2021.03.18 |
| [Spring] Proxy 객체 (0) | 2021.03.12 |
| [Spring] 빈의 라이프 사이클 (0) | 2021.03.10 |
| [Spring] 컴포넌트 스캔 (0) | 2021.03.09 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- sweeping
- dijkstra
- 펜윅트리
- 이분탐색
- spring
- dfs
- 세그먼트트리
- 트라이
- knapsack
- string
- 2-SAT
- Oracle
- Segment tree
- Suffix Array
- union find
- SCC
- Fenwick
- 정렬
- kmp
- 좌표압축
- 동적계획법
- DP
- spring boot
- bfs
- implementation
- 이분매칭
- 스위핑
- hld
- sorting
- greedy
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
